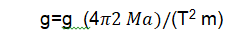Apparatus:
A helical spring of proper value of K, Iron stand, slotted weights, stop watch.
Observations and Calculations:
| No.of abs | Oscillating mass ‘M’ gms | Time for 10 vibrations | Time period T=t/20 | Extension Produced Weights in gms ‘a’ cm | ||
| 1 sec | 2 sec | Mean ‘t’ sec | ||||
| 1 2 3 |
20 40 60 | 20 20 20 | ||||
Mean value of ‘g’=………………………cm/s
Procedure:
1. Suspended a helical spring from a clamp of an iron stand. Attach the hanger at lower end of spring. Load this hanger with different weights.
2. Note the extension on scale (X).
3. Make it vibrate by pushing then hanger downward and note the time for 20 vibrations twice and take its mean value.
G=4 (M/m) xax (1/T2 ) and find value of ‘g’ 4. Repeat this experiment twice more, for the different value of load and find its time for 10 vibrations respectively. Also find the extension for the same mass ‘m’. Find the value of ‘g’ in each case and take its
VIVA VOCE
Q: 1 What is meant by restoring force?
A- The Force which brings the system back towards its mean position is called restoring force.
Q: 2 What are the responsible factors of oscillatory motion?
A: The responsible factors of oscillatory motion are:
- Restoring force (ii) Inertia
Q: 3 what is SHM?
A: The oscillatory motion for which acceleration is directly proportional to displacement and is always towards the mean position.
Q: 4 What is meant by force constant or spring constant?
A: The ratio of force exerted on the spring to the extension produced it is called force constant of the spring. [i.e.k=]
Q: 5 Define elastic limit.
A: It is the limiting value of stress beyond which the body does not obey hook’s law.
Q: 6 State hooks. S law
A: Its states that within elastic limit. The force exerted on a spring is directly proportional to the extension produced in it.
Q: 7 What do you meant by helical spring?
A: A spring wounded in a form of helix is called helical spring.
Q: 8 What type of energy is stored in the spring when stretched or compressed?
A: The energy is stored in the spring when stretched or compressed will be elastic potential energy.
Q: 9 Define stress and strain.
A: Steass: Force applied to body per unit area is called stress .Strain: The ratio of change produced by the deforming force to the original length or volume or shape of a body is called strain.
Q: 10 write down characteristics of SHM.
A: The characteristics of SHM are:
- Acceleration is directly proportional to the displacement form the mean position.
- Acceleration is always directed towards the mean position
- Total energy of SHM remains conserved.
Q: 11 How the value of “g” can be calculate form mass spring system?
A: Calculate the extension “x” is the spring by loading it. Then calculate the time period “T” of one oscillation finally “g” is measured by