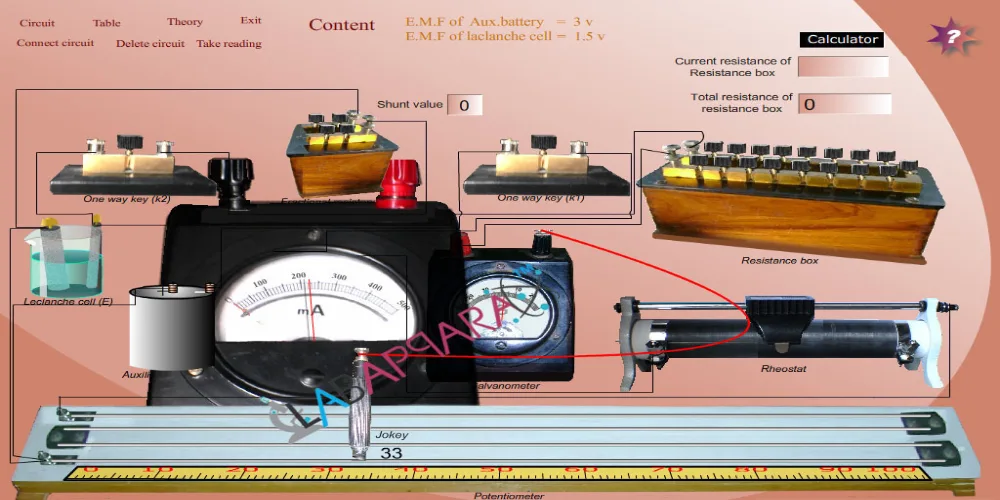
Experiment to determine the emf of a cell using a potentiometer, including apparatus, theory, procedure, precautions, and viva questions with answers.
Apparatus
Potentiometer, 3-volt battery, Leclanché cell, galvanometer, rheostat, one-way key, two-way key, voltmeter, connecting wires, and sandpaper.
Theory
A potentiometer works on the principle that the potential difference across a uniform wire is directly proportional to its length when a constant current flows through it.
When key K₁ of the two-way key is closed, the EMF (E₁) of the first cell is proportional to the balance length l₁.
When key K₂ is closed, the EMF (E₂) of the second cell is proportional to the balance length l₂.
Therefore,
E2E1=l2l1\frac{E₂}{E₁} = \frac{l₂}{l₁}E1E2=l1l2
This simple relationship allows the EMFs of two cells to be compared accurately and efficiently.
Procedure
-
First, draw a neat circuit diagram and connect all components correctly.
-
Next, measure the EMF of the Leclanché cell using a voltmeter.
-
Then, close the key K of the potentiometer and K₁ of the two-way key. Touch the jockey to both ends of the wire (A and B) to ensure the galvanometer deflection reverses.
-
After that, find the balance point P when K₁ is closed and record the balance length l₁. This length represents the EMF of the Leclanché cell.
-
Now, open K₁ and close K₂ of the two-way key. Find the new balance point P and note the balance length l₂, which corresponds to the EMF of the Daniell cell.
-
Finally, calculate the EMF of the Daniell cell using the formula:
E2=E1×l2l1E₂ = E₁ \times \frac{l₂}{l₁}E2=E1×l1l2
-
To ensure accuracy, slightly adjust the rheostat and repeat the readings for consistency.
Observation and Calculation

Mean emf =………volts
Result
The ratio of the EMFs of the two cells is found to be:
E2E1=l2l1\frac{E₂}{E₁} = \frac{l₂}{l₁}E1E2=l1l2
Hence, the EMF of the unknown cell is determined accurately.
Precautions
-
Always ensure that the battery EMF is greater than the EMFs of both cells.
-
Measure the balance length from the positive terminal of the battery and both cells.
-
Remove the plugs from the keys immediately after noting readings.
-
Keep the rheostat at minimum resistance while experimenting.
-
Avoid parallax error when observing the balance point.
Viva Questions and Answers
Q1: What is a potentiometer?
Ans: A potentiometer is an instrument used to compare and measure potential differences accurately without drawing current from the circuit.
Q2: What is the principle of the potentiometer?
Ans: The potential difference across any length of a uniform wire is directly proportional to its length when a constant current flows through it.
Q3: What is the difference between a potentiometer and a rheostat?
Ans: A potentiometer controls voltage, while a rheostat controls current.
Q4: Can a rheostat act as a potential divider?
Ans: Yes, a rheostat can act as a potential divider in a circuit.
Q5: What is a primary cell?
Ans: A primary cell converts chemical energy directly into electrical energy.