Apparatus
- Cathode ray oscilloscope • DC voltmeter • AC voltmeter step – down transformer battery • rheostat • key and connecting wires.
Theory
The voltage required to produce one small division of deflection of the light spot on the screen of an oscilloscope is called its sensitivity.
When an oscilloscope is switched on a spot of light appears on its screen provided its time based circuit is switched off. This light spot can be centered on the screen with the proper adjustment of Y-shift and X-shift knobs fig. 17(a). If a known DC voltage l is applied to the vertical input terminals. The light spot moves on screen through a certain number of small division say N. the ratio v”N gives the sensitive s” of the oscilloscope. If now the unknown DC voltage V is applied to the vertical input terminals and the shift 0 of the spot is measured. The value of V is given by V=
If a known AC voltage is connected to the vertical input terminals. A vertical line appears on the screen provided the time base is switched off (fig.17.b). the length L” of this line is measured which is proportional to twice the peak value V” (i.e.L”2V”).we can therefore write
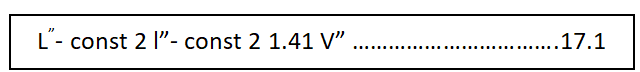
V ̕ the rms value value of the known AC voltage is equal to the reading of the AC voltmeter (fig. 17.b). If now the known AC voltage whose peak value Vr required, is measured, then we can write

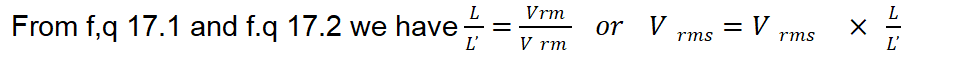
The peak value of the unknown Vr is given by:
Vp = 1.4l Vrms
Procedure
- Clean the ends of connecting wires and arrange the apparatus as shown in fig. 17. (a) Where a known DC voltage which is measured by the voltmeter V, is applied to the vertical input terminal of the oscilloscope.
- Switch on the oscilloscope. With time base switched off a bright spot appears on the screen. With the help of the vertical and horizontal adjustment knobs bring the spot in the center of the screen.
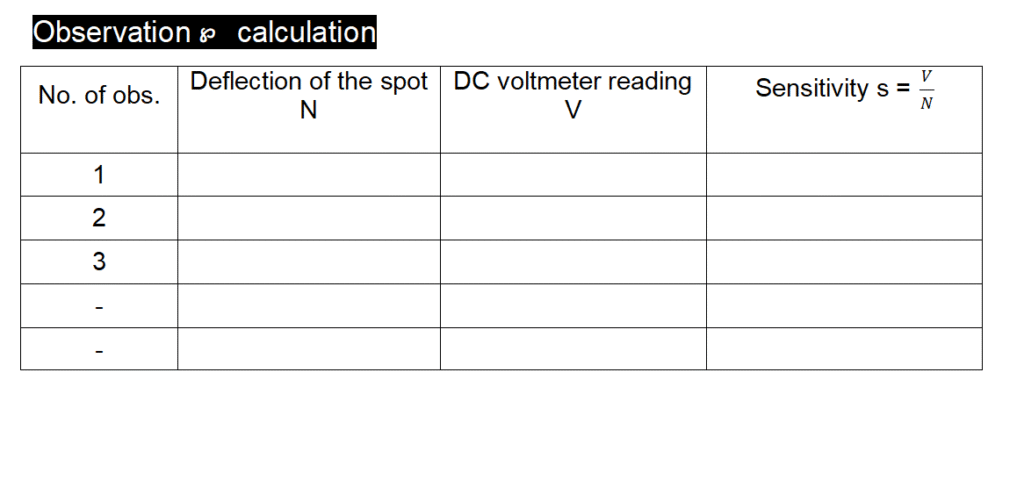
- Plug in the key K and adjust the potential divider so as to get a deflection of the spot along the vertical axis equal to say N small divisions. Take the reading V̕ of the voltmeter: V̕ /N gives the sensitivity S (=V̕ / N) of the oscilloscope. Repeat the above operation with different values of known DC voltage V̕ and find the mean values of S.
- Disconnect the circuit shown in fig. 17(A) from the oscilloscope and connect the unknown DC voltage to the vertical input terminal without disturbing the setting of Y-shift and X-shift knobs note the deflection Ө of the light spot. The unknown DC voltage V is given by
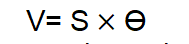
- Now arrange the apparatus as shown in fig.17 (a) where T is a Verica (variable step down transfer) and V is an A.C voltmeter. The output voltage wires ww̕ of the transfer are connected to the vertical input terminal of the oscilloscope. Connect the transformer T with A.C mains. With the time base switched off a vertical line is obtained on the screen. Bring this vertical line in the center of the screen and measure its length L̕. This is proportional to twice the peak values V̕ or twice the ms values V̕rms of the known AC voltage. Note the reading of the AC volte which gives the values of V̕rms.
- Disconnect the circuit shown in fig.17 (b) from the oscilloscope and connect the unknown AC voltage to the vertical input terminals. Without disturbing the setting of the oscilloscope a vertical line again appears. Centre this line and measure its length L. the rms values of the unknown voltage (V̕rms )is given by
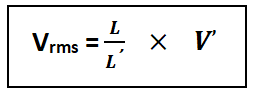
And its should be equal to the reading of the AC voltmeter.
The peak values of the unknown AC voltage is given by
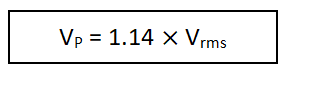
Means value of S = ………………
Reflection with unknown DC voltage Ө = ………….
Unknown DC voltage V = S Ө
= …………. Volt
Determination of AC voltage:
Known AC voltage = V ̕rms =……………. volt
Length of the line with known AC voltage =L̕ = ……….. divisions
Length of the line with unknown AC voltage = L = ……… division
Rms value of the unknown voltage = Vrms = v̕rms =……….volt
Rms value of the unknown voltage as given by AC voltmeter =………volt
Peak value of the unknown voltage Vp = 1.41Vrms =…………..volt
Procedure
- Connection should be clean and tight.
- Light on the screen should be as fine as possible.
- Deflection of the spot should be in whole numbers.
- The setting of y- shift knob should not be disturbed while taking reading in each part of the experiment.
Viva voce
Viva voce
| Q .1 what is a cathode ray oscilloscope? Ans. Cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) is an electronic instrument which produce a visual representation of the relation between two or more variable on a fluorescent screen. Q .2 Distinguish between a direct current (DC) and an alternating current? Ans. A direct current flows in one direction in a circuit and its strength remains constant. On the other hand an alternating current change periodically both in strength and direction. It increases from zero to a maximum and then decreases to zero. It then reverses its direction, increases from zero to maximum in the reverse direction and then decrees to zero. This sequence Of the events, called a cycle, is repeated. |
| Q .3 Define impedance? Ans. Impedance of a circuit is the total opposition to the flow of alternating current. Q .4 what is meant by an electron gun? Ans. The group of electrodes which produce a fine beam of electron in a C.R.O or other instruments is called an electron gum. |