Apparatus:
Vernier calipers, Solid cylinder.
Diagram:
Point to Ponder:
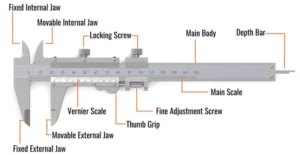
Vernier callipers is used for measuring the length and diameter accurately up to 10 – 1 mm. A vernier callipers consists of a rectangular steel bars graduated in inches on one edge and in centimeters on the other edge this is known as the main scale. Over this scale slides a small scale called the vernier scale.
There are two jaws upper and lower, the upper jaws are used to measure the internal diameter of the tubes. The lower jaws are used to measure the external diameter of rods, tubes etc. It has also a thin rectangular rod on back, which is used to measure depth of vessels.
Vernier Constant:
The difference between one main scale division and one vernier scale division is called vernier constant. Usually when the jaws are, closed, the zero of the main scale concider with the zero of the vernier scale, then there is no error. If this is not so then the calliper have a zero error. There are two types of zero error:
(i) Positive error
(ii) Negative error
Zero Error
Positive Error:
If zero line of vernier scale lies ahead (OR on right side) of zero line of main scale, then zero error will be positive. In order to find the value, observe the number of division on vernier scale which coincides with any main scale division and this division is multiplied by least count, say, 4th division of v. scale coincides with any main scale division then
Zero error = +4 L.C.
= +4 0.01 cm
= 0.04 cm
Zero correction = _ 0.04 cm
Negative Error:
If zero line of vernier scale lies behind (OR on left side) of zero line of main scale, then error will be negative. In order to find its value, observe number of division of vernier scale which coincides with any main scale division, subtract it from 10 and result is multiplied by least count, say, 4″ division of scale is coinciding with any main scale division, then
Zero error = – (10 – 4) x L.C.
= -6 x 0.01 cm
= -0.06 cm 7
Zero correction = + 0.06 cm
Procedure:
Find least count or vernier constant of vernier callipers. Then find zero error.
Now put the given cylinder lengthwise into the lower jaws and tight the screw of vernier scale that the jaws remain fixed. Observe the main scale division just to the left of zero line of vernier scale. This will give main scale reading R. Now to find fraction to be added ‘y’ second which of vernier scale div. coincides with any main scale division, n. multiply this no. by least count and then added to main scale reading R. This will give length of cylinder.
Similarly find diameter and then radius of cylinder. Finally calculate volume by using formula.
V = πr2
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS:
For calculation of length
Length:
| No.of Obs | Main scale reading R |
No. of Vernier scale div. Coinciding with any main Scale division (n) |
Fraction to be Added Y = n L.C. |
Observed Length = y + R | Corrected Length Z.C |
| cm | div. | cm | cm | cm | |
| 1 2 3 4 |
Mean length of cylinder = l = ……… cm
Diameter:
| No.of Obs | Main scale reading R |
No. of Vernier scale div. Coinciding with any main Scale division n |
Fraction to be Added Y = n L.C. |
Observed Length = y + R |
Corrected Length Z.C |
| cm | div. | cm | cm | cm | |
| 1 2 3 4 |
Mean diameter of cylinder = d = ……… cm
Radius of cylinder = r = d/2 = ……. cm.
Volume of cylinder = V = πr2l = ……..cm³.
The volume of cylinder = V = ……..cm3.
(1) Find volume of a test tube by using Vernier Callipers.
(2) Find volume of a solid sphere by using Vernier Callipers.
Precautions:
(1) Jaws should not be pressed too much.
(2) Tight the screw of Vernier scale before taking the reading.
VIVA VOCE
Q.1 What is vernier constant or L.C.?
Ans. The smallest (measurement) reading which a vernier calliper can read is called vernier constant
Q.2 What are the various parts of a vernier calliper?
Ans. Vernier calliper has three parts:
(i) Upper Jaws: For the measurement of the internal diameter of a pipe, ring or cylinder.
(ii) Lower Jaws: For the measurement of the external diameter of rod, pipe or ring.
(iii) Depth Gauge: The sliding bar is used for measuring the depth of the vessel.
Q.3 What is advantage of vernier calliper over a regular graduated in millimeters?
Ans. We can measure upto millimeter with regular scale which is graduated in millimeters when with vernier calliper, we can measure upto 0.1 mm accurately.