An experiment studies current vs. potential across a tungsten filament, showing deviation from Ohm’s law as resistance increases with temperature.
Apparatus
Battery (12V), tungsten lamp (12V, 25W), rheostat, voltmeter, ammeter, key, connecting wires, and sandpaper.
Theory
According to Ohm’s law, the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it, provided temperature remains constant.
However, in a tungsten filament lamp, as the voltage increases, the filament heats up. Consequently, its resistance also increases, causing the relationship between voltage and current to become non-linear. Therefore, tungsten does not obey Ohm’s law at high temperatures.
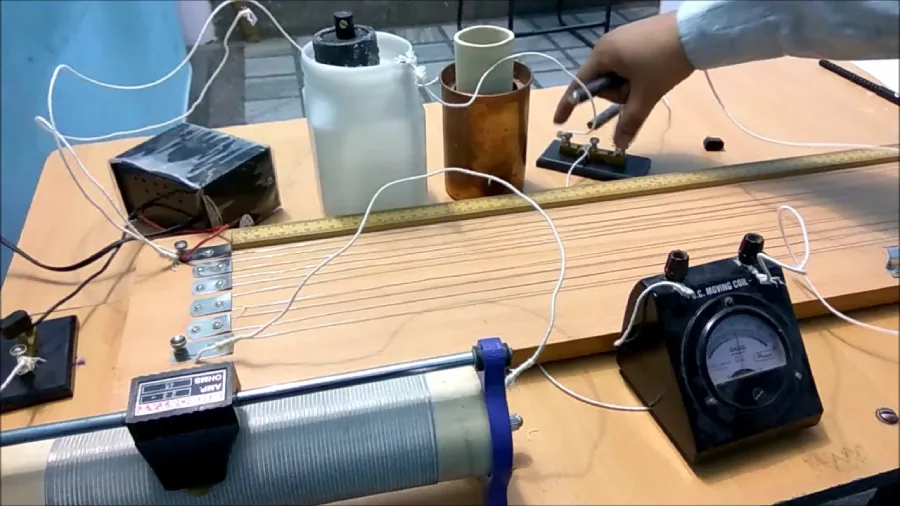
Procedure
-
Draw the circuit diagram and connect all components as shown. The rheostat acts as a potential divider. Connect the ammeter in series with the tungsten bulb and the voltmeter in parallel to it.
-
Insert the plug key to allow current to flow through the bulb. Then, note the readings of the voltmeter (V) and ammeter (I).
-
Gradually change the potential difference across the bulb by sliding the rheostat terminal. Record at least eight to ten readings for different voltages.
-
Plot a graph between V and I, taking V along the x-axis and I along the y-axis. The curve obtained is non-linear, showing that the tungsten filament does not obey Ohm’s law.
Observation and Calculation

Conclusion
The graph between V and I is a curve, not a straight line. Therefore, the tungsten filament bulb does not obey Ohm’s law, as its resistance increases with temperature.
Precautions
-
Ensure all connections are clean and tight.
-
Use a high-resistance rheostat for better control.
-
Change the voltage in small and regular steps for accuracy.
Viva Voce
Q1: State Ohm’s law.
Ans: The potential difference across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided temperature remains constant.
Q2: Does a tungsten filament obey Ohm’s law?
Ans: No. The filament’s resistance increases with temperature, so it does not obey Ohm’s law.
Q3: What is electric current?
Ans: Electric current is the amount of charge passing through a conductor per unit time.
Q4: Define resistance and state its unit.
Ans: Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electrons in a conductor. Its SI unit is the Ohm (Ω).
Q5: What is the relation between I and V for a tungsten filament?
Ans: The relation between I and V is non-linear because the resistance of the filament changes with temperature.
Q6: Which is a base unit in the SI system — coulomb, ampere, or volt?
Ans: The ampere is a base unit in the SI system.